There Are Countless Membranes, But We Will Only Choose The Ones You Need.
- Ultrafiltration Membranes (UF):Pore size 0.01-0.1 µm, mainly removes suspended solids, bacteria, and large molecular organic compounds. Suitable for municipal and industrial wastewater pretreatment, high-pollution water treatment.
- Microfiltration Membranes (MF): Pore size 0.1-1 µm, removes suspended particles and oils. Applied to food industry wastewater and municipal sewage treatment.
- Nanofiltration Membranes (NF): Pore size for molecular weight 200-1000 Dalton, used for hardness removal and organic matter separation.
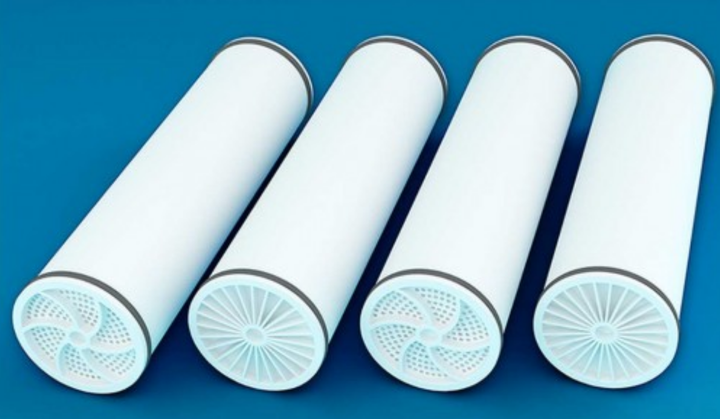

- Reverse Osmosis Membranes (RO): Pore size <0.0001 µm, removes dissolved salts, metals, and organic pollutants. Widely used in industrial wastewater reuse and seawater desalination.
- Electrodialysis Membranes (ED): Separates ionic compounds, ideal for high-salinity wastewater treatment, applied in the chemical industry for desalination.
- Membrane Bioreactor Membranes (MBR): Combines biological degradation and membrane filtration, suitable for high COD wastewater treatment, energy-efficient membrane systems for municipal and industrial wastewater.
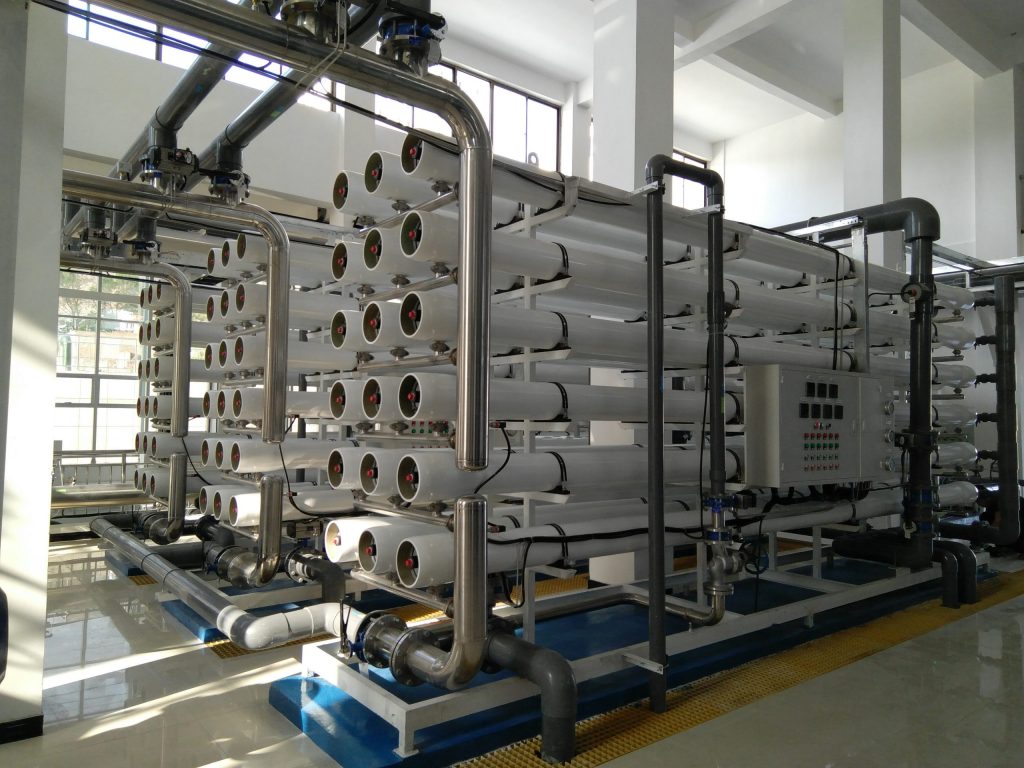

Classification And Products Of Membranes For Exhaust Gas Treatment

- Gas Separation Membranes
- Characteristics: Used for specific gas separation, such as CO₂, hydrogen, and VOC recovery.
- Materials:
- PEEK (Polyetheretherketone): High-temperature gas treatment.
- Polyamide Membranes: VOC separation.
- Selective Permeation Membranes
- Characteristics: Separates toxic gases such as H₂S and SO₂.
- Materials:
- Composite Membranes: Low-concentration VOC separation.
- Membrane Distillation Membranes
- Characteristics: Uses evaporation to separate gaseous pollutants.
- Hydrophobic Membranes: Used for high-temperature waste gas treatment.
- Degassing Membranes
- Characteristics: Removes dissolved gases like oxygen and nitrogen from waste gases.
- Materials:
- Hollow Fiber Membranes: Efficient degassing.
